In the pursuit of fitness, most people focus on workouts, nutrition, and supplementation. However, one crucial factor often overlooked is sleep and recovery. Training hard in the gym without adequate rest can stall progress, increase the risk of injury, and lead to burnout. Sleep is not just “downtime”—it’s when the body repairs, rebuilds, and grows stronger. Understanding the connection between sleep, recovery, and fitness gains is key to optimizing performance.
This blog explores the sleep fitness benefits, the connection between sleep and weight loss, how much sleep is required for muscle growth, and practical sleep hacks for athletes to maximize recovery. By the end, you’ll understand why sleep might just be the most powerful (and free) performance enhancer available.
Why Sleep Matters for Fitness
The Science Behind Sleep
Sleep is a highly structured biological process that occurs in cycles. Each sleep cycle lasts about 90 minutes and consists of four stages:
- Light Sleep (Stage 1 & 2): Transitional phase, body starts relaxing.
- Deep Sleep (Stage 3): The most restorative stage where tissue repair, hormone release, and immune strengthening occur.
- REM Sleep: Critical for brain function, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.
When you sleep, your body enters cycles of deep sleep and REM sleep, each playing a unique role in recovery and performance.
Sleep Fitness Benefits
- Muscle Repair & Growth: During deep sleep, growth hormone (GH) peaks, triggering muscle repair and hypertrophy.
- Improved Recovery: Sleep reduces inflammation and replenishes glycogen stores.
- Hormonal Balance: Adequate sleep regulates cortisol (stress hormone), testosterone, and insulin sensitivity.
- Enhanced Performance: Athletes with sufficient sleep have better reaction time, focus, and strength.
- Injury Prevention: Poor sleep quality is linked to slower reaction times and increased risk of accidents.
Simply put: without quality sleep, your training results will always be limited.
Sleep Cycle and Weight Loss Connection
Many overlook the link between sleep and fat loss, focusing only on diet and cardio. But sleep is a hidden driver of body composition.
The Role of Hormones
- Leptin & Ghrelin: Sleep deprivation reduces leptin (satiety hormone) and increases ghrelin (hunger hormone), making you crave high-calorie foods.
- Insulin Resistance: Lack of sleep lowers insulin sensitivity, leading to fat storage.
- Cortisol Spike: Chronic sleep debt raises cortisol, which promotes fat gain, especially around the abdomen.
Research Findings
- People who sleep fewer than 6 hours a night are 30% more likely to be obese.
- In one study, dieters who slept 8 hours lost more fat, while those who slept 5 hours lost more muscle.
Takeaway: If you want to burn fat and preserve muscle, sleep is just as important as nutrition and exercise.
How Much Sleep for Muscle Growth?
The question often arises: how much sleep do you really need to build muscle?
General Guidelines
- Adults: 7–9 hours per night
- Athletes: 8–10 hours per night
Why Athletes Need More Sleep
Athletes subject their bodies to higher stress loads, requiring more recovery. Professional athletes like LeBron James and Roger Federer reportedly sleep 10–12 hours per night, proving its role in elite performance.
Sleep Debt and Muscle Growth
Consistently cutting sleep short—even by an hour—accumulates sleep debt, which impairs recovery and muscle protein synthesis. Over time, this leads to:
- Slower strength gains
- Reduced endurance
- Increased injury risk
Optimal Range: Aim for 8–9 hours for muscle growth and serious training.
Circadian Rhythm and Fitness
What is the Circadian Rhythm?
The circadian rhythm is the body’s internal clock, regulating sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, digestion, and metabolism. Disrupting this rhythm (like staying up late or shift work) can significantly affect recovery.
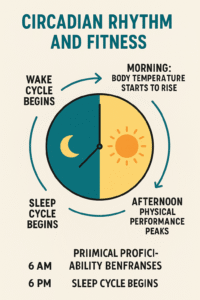
Impact on Fitness
- Morning Workouts: Align with cortisol peaks for alertness.
- Evening Workouts: Can enhance strength performance due to elevated body temperature.
- Night Shift Workers: Struggle with recovery and often experience higher fat gain due to circadian misalignment.
Tips to Align Circadian Rhythm
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule (even on weekends).
- Get morning sunlight exposure to reset your biological clock.
- Limit blue light exposure at night to improve melatonin production.
Deep Sleep and Muscle Repair
Why Deep Sleep is the “Anabolic Window”
Most people focus on the post-workout anabolic window, but the real muscle-building happens at night during deep sleep:
- Growth hormone surges
- Protein synthesis accelerates
- Muscle fibers repair from microtears
- Immune system boosts recovery
Factors Affecting Deep Sleep
- Alcohol & Caffeine: Reduce time spent in deep sleep.
- Stress & Cortisol: Prevent deep restorative rest.
- Overtraining: Can disrupt sleep patterns due to high nervous system activity.
Hacks to Maximize Deep Sleep
- Maintain a cool room temperature (18–20°C).
- Avoid stimulants at least 6 hours before bed.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine (stretching, reading, meditation).
Sleep Hacks for Athletes
Athletes can benefit from specific strategies to optimize sleep and recovery.
1. Nap Smartly
- Power Naps (20–30 minutes): Improve alertness and performance.
- Long Naps (90 minutes): Complete a full sleep cycle for deeper recovery.
2. Optimize Pre-Bed Nutrition
- Include foods rich in tryptophan (turkey, milk, nuts).
- Casein protein before bed provides a slow-release amino acid supply.
- Avoid heavy meals and sugar late at night.
3. Use Sleep Supplements Wisely
- Melatonin: Helps regulate circadian rhythm.
- Magnesium: Supports relaxation and muscle recovery.
- ZMA (Zinc, Magnesium, B6): Popular among athletes for recovery.
4. Create the Perfect Sleep Environment
- Blackout curtains for darkness
- White noise machine or earplugs to block disturbances
- Comfortable mattress and pillow suited for your body type
5. Track and Improve
- Use sleep trackers (Oura Ring, WHOOP, Apple Watch) to monitor sleep quality.
- Adjust habits based on data (bedtime consistency, alcohol reduction).
Common Sleep Cycle Problems in Athletes
Insomnia
Often caused by stress, overtraining, or poor sleep hygiene. Solution: relaxation techniques, consistent sleep routine.
Sleep Apnea
Common in heavy lifters with large neck circumference. Solution: medical consultation, CPAP devices.
Jet Lag
For traveling athletes, time zone shifts affect circadian rhythm. Solution: light exposure, melatonin, gradual adjustment.
Importance of Sleep and Recovery in a Training Program
Recovery is more than just resting. It’s an integrated part of a training cycle.
- Training + Nutrition + Sleep = Growth
- Skipping sleep is like skipping workouts—it sabotages progress.
- Coaches now prioritize sleep in athlete programs, calling it the “third pillar of fitness.”
Action Plan: Sleep Optimization Checklist
Here’s a practical checklist to improve sleep and recovery:
- Consistency: Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
- Darkness: Use blackout curtains and avoid screens before bed.
- Temperature: Keep room cool (18–20°C).
- Nutrition: Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and heavy meals late.
- Relaxation: Stretch, meditate, or journal before bed.
- Tracking: Use wearable devices to monitor progress.
Conclusion
Sleep isn’t optional if you want serious fitness results—it’s essential. While workouts and nutrition get most of the attention, it’s during deep sleep that muscles repair, hormones balance, and the body recovers. From regulating weight loss hormones to fueling muscle growth, sleep is the ultimate recovery tool.
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts must prioritize 7–9 hours of quality sleep every night, align their circadian rhythm, and adopt proven sleep hacks for optimal performance. Remember: your progress in the gym is only as strong as your recovery outside of it.
Final Thought: If you want to maximize gains, don’t just train harder—sleep smarter. Check Trainwithrahul for more in information and fitness plan.
FAQs
1. How much sleep do I need for muscle growth?
Athletes and those engaged in intense training should aim for 8–10 hours of sleep per night. While the general recommendation is 7–9 hours for adults, those building muscle need extra time for muscle repair and recovery. Professional athletes often sleep 10–12 hours to support elite performance.
2. Can lack of sleep affect weight loss?
Yes, absolutely. Sleep deprivation disrupts hunger hormones (leptin and ghrelin), increases cravings for high-calorie foods, and raises cortisol levels, which promotes fat storage. Studies show that people sleeping fewer than 6 hours are 30% more likely to be obese. Quality sleep is essential for fat loss and maintaining healthy body composition.
3. What is deep sleep and why is it important for athletes?
Deep sleep (Stage 3) is the most restorative sleep stage where growth hormone peaks, muscle repair occurs, and the immune system strengthens. It’s when protein synthesis accelerates and muscle fibers heal from microtears caused by training. Without adequate deep sleep, recovery is compromised and muscle growth slows down.
4. Does napping help with muscle recovery?
Yes! Power naps (20–30 minutes) can improve alertness and performance without causing grogginess. Longer naps (90 minutes) allow you to complete a full sleep cycle, providing deeper recovery benefits. Many elite athletes incorporate strategic napping into their training programs.
5. What are the best sleep hacks for athletes?
Key sleep hacks include:
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
- Keeping your bedroom cool (18–20°C)
- Using blackout curtains and minimizing blue light exposure
- Avoiding caffeine 6+ hours before bed
- Taking magnesium or ZMA supplements
- Consuming casein protein before bed
- Using sleep trackers to monitor sleep quality
6. How does sleep affect athletic performance?
Quality sleep enhances reaction time, focus, strength, and endurance. It also supports hormonal balance (including testosterone and growth hormone), improves decision-making, and reduces injury risk. Sleep-deprived athletes experience slower recovery, decreased performance, and higher accident rates.
7. What is circadian rhythm and how does it affect fitness?
Your circadian rhythm is your body’s internal clock that regulates sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, and metabolism. Disrupting it (through irregular sleep, shift work, or excessive blue light) impairs recovery and can lead to fat gain. Aligning your training schedule and sleep patterns with your circadian rhythm optimizes performance and recovery.
8. Can I build muscle if I only sleep 6 hours a night?
While possible, muscle growth will be significantly compromised with only 6 hours of sleep. This amount of sleep leads to sleep debt, impairs muscle protein synthesis, reduces growth hormone release, and increases cortisol levels. For optimal muscle building, aim for at least 8 hours consistently.
9. What supplements can improve sleep quality for athletes?
Popular sleep supplements for athletes include:
- Melatonin (regulates circadian rhythm)
- Magnesium (promotes relaxation and muscle recovery)
- ZMA (Zinc, Magnesium, Vitamin B6 for recovery)
- L-theanine (reduces stress)
- Glycine (improves sleep quality)
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting new supplements.
10. How can I track my sleep quality?
Use wearable devices like:
- Oura Ring (detailed sleep tracking)
- WHOOP (recovery-focused metrics)
- Apple Watch (sleep stages and trends)
- Fitbit (sleep score and patterns)
- Garmin devices (comprehensive health metrics)
These sleep trackers monitor sleep stages, heart rate variability, and recovery, helping you optimize your sleep habits.